Azure provides many options for data ingestion and Azure data factory is one of them. It is an option for scenarios where you need to transfer data regularly or in technical terms it is cloud data integration service known as data pipeline. Azure data factory works on two key pillars, i.e. data movement and data transformation. This cloud based data integration service allows to create data-driven workflows and orchestration/automation of the data movement and transformation processes.
Courtesy: Microsoft
Let me explain you this through one scenario:
One of the super market is going through the transformation and looking for ways to increase the revenue and customer satisfaction. Many stores are doing well in terms of revenue and customer satisfaction while few stores are struggling to achieve the same. Business has decided to close few existing stores and open new stores in new locations as well. Super market stores capture the customer satisfaction by a survey machines installed on each PoS system. When customer makes the payment, cashier request them to provide a feedback. This feedback system runs on cloud-native app and store the data directly to the cloud in synchronous mode. This organization wants to analyze userbase based on the demographics. All the billing related data is being stored in ERP system that resides in on-premises datacenter.
Strategy team has provided an approach to generate and visualize useful data for new markets. To fulfill this need, you need to consolidate all the data in one place and because of the continuity, it is not one-time job as they need to compare data based on the days, weeks, month, year, time and season wise. With Azure Data Factory you can move your data continuously using data pipeline, and once data has been moved there then you can first transform this data based on the need and later use this data with any systems or use analytics tools like Power BI to visualize the data. Here is the process, which differs between version 1 and 2.
Azure Data Factory v1:

Azure Data Factory v2:

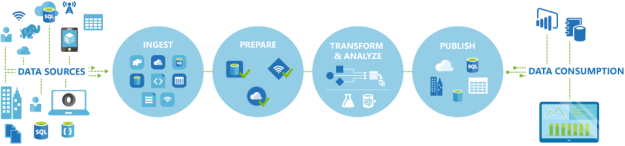
Now let’s understand the process in detail:
Connect & Collect: Whenever you need to play with data, first you need to collect it. In layman language, you can copy the data from multiple sources in different ways such as using some copy utility, FTP/SFTP, scripts etc. This data can be in multiple forms such as structured, un-structured and semi-structured, and can be extracted from multiple sources such as on-premises, SaaS solutions, database, file shares etc. Once you have multiple data sources, frequency and availability of data will also differ. Azure data factory can connect to multiple data sources and collect the data into the centralized data store such as Azure Blob Storage or Azure data lake store etc.
Transform & Enrich: Once the raw data has been collected, you can transform the data using compute services such as HDInsight Hadoop, Spark, Data Lake Analytics and Machine Learning.
Publish: Once you have transformed the data now you can use this valuable data anywhere in the cloud or can send back this data to on-premises as well. This data can be used by any analytics tool such as Power BI to visualize and generate the reports or can be loaded into the Azure Data Warehouse, Azure SQL Database, Azure cosmoDB or anywhere else for further use.
Monitor: Azure Data Factory v2 provides the monitoring capabilities to monitor established data integration pipelines for various purposes. You can leverage built-in support for pipeline monition via PowerShell, log analytics, Azure monitor, API and health panels on the Azure portal.
At present, Azure Data Factory is available in selected regions only. ADF v1 is available in East US, East US2, West US, West Central US and North Europe region while ADF v2 is available in East US, East US2, West US, West Central US, North Europe and West Europe regions. However, a data factory can use compute resources and data stores from other regions as well. Therefore, you can use this service by leveraging ADF from selected regions.
Azure Data Factory pricing can be calculated based on the four parameters:
- Number of activities run.
- Volume of data moved.
- SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) compute hours.
- Whether a pipeline is active or not.
You can calculate your pricing here.
At present, Azure Data Factory version 2 is in preview.